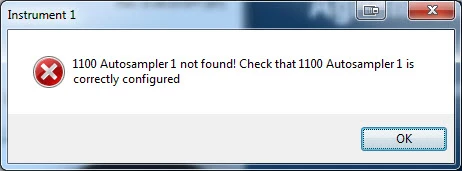
There’s nothing like preparing your samples and starting chemstation, only to see “instrument offline”. There are some basics that can be checked that may be the solution if you are having this problem.
IP addresses:
You always want to start here. A 68/7890 GC, as well as 1100-1290 LCs use LAN communication for the most part. The main idea being, is the ip address of the instrument and the ip address of the pc compatible? You want the ip address to match up until the last set of numbers. For example: if the gc is 10.1.1.101, the pc needs to be 10.1.1.x. If the LC is 192.168.254.11, the pc needs to be 192.168.254.x. With “x” being any digit from 1 to 255.
How can I check the ip address of the GC? This is pretty simple, on the majority of these GCs you can find out by hitting options, then communication on the gc front panel. From here you can see what the address currently is, and you can also change it as well.
The LC is not as straight forward, but the default is 192.168.254.11. You can also connect the gameboy to the module and view/edit the ip address. If it’s not the default, and you are not sure what the address is, then you will have to go through a process of changing switches on the LAN card and setting it to default. From there you can keep the default or change to a new address using Telnet. I may write an article on that procedure in the future.
How can I check the ip address on the pc? You can do this through the control panel of windows, then go to network and internet, then network connections. You can see all your network connections on this screen. Most people will have two connections, a “house” or company network, and a local area connection. The local are connection is usually the one that is connected to the instrument. Right-click on that connection, then double click on IPv4. You will see a screen like this:
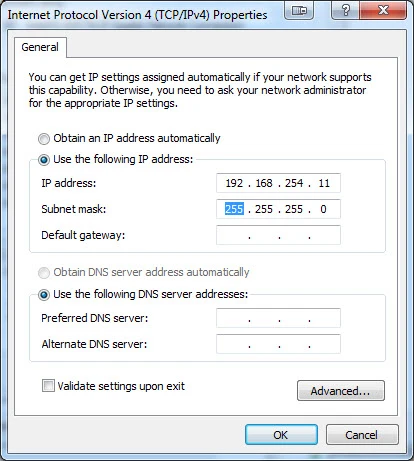
From here you can view and change the IP address. Make sure to keep the subnet mask: 255.255.255.0. Hit OK to save the changes.
After determining that the addresses are compatible, the next thing you want to do is ping the instrument. To do this you need to launch the command prompt. In Windows 7, click on the Start key for windows, in the search bar type CMD and hit enter. In Windows XP, hit start, and select run, type CMD and hit enter.
Once in the command prompt type: ping 10.1.1.101 (or whatever the ip address of the instrument is). You should get 4 replies back, 100% packets sent and received. If not, then check that the cable from the pc to the insturment is connected and good, maybe try swapping it out. If there is a switch or hub in between make sure that port is operational. If there are 2 LAN cards on the pc, its possible that you are connecting to the wrong one, or changed the ip address on the wrong one. Does the LAN card on both the pc and instrument show flashing LED lights on the port? If not it may be a hardware problem with one of the cards.
Configuration:
If pinging the instrument was successful, the last piece of the puzzle is ensuring the configuration in chemstation has the proper ip address for the instrument. If you are using a classic version of chemstation (pre-Openlab), go to start, all programs, agilent chemstation, and launch the configuration editor. From here you can view/edit the ip address of what chemstation thinks the instrument is configured to be. In Openlab chemstation, launch the Openlab control panel, select your instrument on the left hand side, and click on configure instrument on the top of the screen. From here you can view/edit the ip address of what Openlab is expecting your instrument to be configured to be.
I hope these basic steps of checking/pinging the ip address have been helpful. Please leave a comment if you have any feedback or questions, thanks!







Recent Comments